LCD configuration¶
This section describes the steps needed to enable the frame buffer driver for the Industrial I/O host board.
All revisions of the industrial I/O boards will support the LCD connector interface with modules that include an FPGA (e.g., the MityDSP-L138F and MityARM-1808F). Modules without the FPGA CANNOT use the LCD expansion header.
All revisions of the industrial I/O boards will support the DVI interface with modules that include an FPGA.
Revision C and higher of the industrial I/O boards will support the DVI interface with modules that to not include an FPGA (e.g., the MityDSP-L138 and the MityARM-1808).
Step 1 - Enable the Peripheral¶
The current version of u-Boot includes a command to provide hints to the kernel as to how the peripherals (UARTs, SPI, LCD drivers, etc.) should be configured. This code is still being refined, but does support configuration of the LCD (/dev/fb) interface to support a QVGA panel and the DVI interface using 640x480 resolution. The peripheral configuration that is managed by u-boot is set and stored (to the SPI FLASH) via the "config" command.
To see the current configuration, at the u-Boot prompt type:
U-Boot > config MityDSP-L138 Configuration: Config Version : 1.0 Config Size : 228 Manufacturer : Critical Link Ethernet Config : 2 Ethernet Name : GENERIC @ 0x03 Ethernet PHYMask: 8 LCD Config : 1 LCD Panel : vga_640x480
This shows that the u-Boot configuration is configured for the DVI VGA 640x480 mode of operation. If the LCD Config is 0, then no frame buffer device will be created, and the LCD device will be left off.
To add a video configuration, run "config set":
U-Boot > config set
This will prompt you for various configuration items. You can hit return for all of the items to leave them at their default / current setting. When you get to the "LCD Config" prompt, enter a "1". This will result in a prompt for the LCD Panel Type. Currently, you can enter the following options (exactly, these are case sensitive):
- vga_640x480
- wvga_800x480
- Sharp_LQ035Q7DH06
- NEC_NL4827HC19-05B
- svga_800x600
The first will configure the a VGA resolution output at approximately 60 Hz suitable for the DVI controller chip. The second will configure a 60 Hz refresh rate QVGA resolution for the touchscreen panel available from Critical Link (based on the Sharp LCD display with the above mentioned panel -- NOTE this panel is now manufactured under a different part number). Others will be added as needed. For details, check the drivers/video/da8xx-fb.c file and the arch/arm/mach-davinci/board-mityomapl138.c source code in the linux kernel directories.
Once you have set the configuration, you can boot linux for testing. However the configuration will be lost on the next boot. To save the configuration, you need to issue the command:
U-Boot > config save
This will store the configuration off to disk. NOTE: this may not be the way peripherals will be configured in the future, but it is what was put together to solve an immediate issue. Future versions of the kernel and boot loader may use a different technique based upon input from the larger linux community and the availability of the device tree for ARM based processors.
The kernel should configure the LCD on boot up. Usually, the udev will find and automatically configure the /dev/fb device. However, there have been reports of udev timing out before completing the operation. If you do not see a /dev/fb0 (or a /dev/fb) device, you can create a link with the following commands:
root@mityomapl138:~# cd /dev root@mityomapl138:/dev# mknod /dev/fb0 c 29 0 root@mityomapl138:/dev# chgrp video fb0 root@mityomapl138:/dev# chmod g+w fb0 root@mityomapl138:/dev# ln -s fb0 fb root@mityomapl138:/dev# ls -l /dev/fb* lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 3 Apr 9 14:01 /dev/fb -> fb0 crw-rw-r-- 1 root video 29, 0 Apr 9 14:01 /dev/fb0
Step 2 - Load FPGA to Route LCD signals to Host Board(FPGA modules only)¶
Once the kernel has configured the LCD display, the LCD video signals from the OMAP-L138 need to be routed to the host board DVI interface (or conditioned and routed to the LCD interface). Therefor, you must load an appropriate FPGA image for the video to show up on the device.
Links to FPGA reference projects and downloadable .bin files for using the Critical Link provided QVGA LCD or the DVI interface are included below.
Step 3 - DVI configuration¶
The DVI converter on the Industrial I/O board includes an I2C interface as well as the 16 bit video interface. By default, the DVI converter chip comes up in a power saving mode, so the DVI output is disabled (even though the LCD interface may be running video to it's input). The chip must be commanded on as well as configured via the I2C port interface. On Revision A and B boards, the I2C interface is connected to the FPGA, and requires FPGA drivers to be loaded to communicate with the part. On revision C and higher boards (post 2010), the OMAP-L138 SoC based I2C0 port is connected to the DVI interface (allowing configuration with modules that do not include an FPGA).
To program/enable the DVI converter from within linux after you've booted, you will require a i2c communication utility. The standard I2C utilities package will work (see below) and should be included in the rootfilesystem images provided on the board support packages (MDK). If not, you can install them on a network connected module with the command described below.
If you are using a Revision C and higher board (post 2010 order), then you can optionally program the chip from within u-Boot without using the i2c utilities. This is convenient in that it allows the display of the linux console and or splash screens during the boot process. See the section below for details.
Installing the linux I2C utilities¶
The easiest way to install the I2C utilities is to put the MityDSP-L138/Industrial I/O board on the network with a connection to the internet. You then directly download and install the necessary i2c package with the following commands:
root@mityomapl138:~# opkg update root@mityomapl138:~# opkg install i2c-tools
On the update, you can ignore the message:
Collected errors: * opkg_download: Failed to download http://www.angstrom-distribution.org/feeds/unstable/ipk/glibc/armv5te/machine/mityomapl138/Packages.gz, wget returned 1.
However, if on the update command you get errors claiming that it was unable to find www.angstrom-distribution.org, then you need to edit the file in "/etc/resolv.conf" and add the line:
nameserver 192.168.1.1
Where you would to replace the ip address above with the nameserver on your network.
Instructions for Revision A & B Boards¶
Once you have the i2c utilities loaded, you now need to add the fpga bus controller driver and the fpga i2c driver modules to the runtime in order to enumerate the i2c driver connected to the DVI controller chip. Drivers module images (.ko images) are included in the tarball on this link. Sources for all FPGA drivers will be made available in the near future.
The procedure listed below should be rolled into a start script for your application.
root@mityomapl138:~# insmod fpga_ctrl.ko root@mityomapl138:~# insmod fpga_i2c.ko root@mityomapl138:~# echo 1 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOUR FPGA IS NOT ALREADY PROGRAMMED BY UBOOT, resets the FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# echo 2 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOUR FPGA IS NOT ALREADY PROGRAMMED BY UBOOT, programs the FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# cat YourFPGAImage.bin > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/image #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOU ARE PROGRAMMING THE FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# echo 3 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd # do this to probe the FPGA for the I2c controller device root@mityomapl138:~# i2cset -y 2 0x38 0x8 0xb9 root@mityomapl138:~# i2cset -y 2 0x38 0x33 0x30
Instructions for Revision C Boards.¶
From U-Boot¶
If you have configured u-Boot to load your FPGA (if using a SOM with an FPGA, not needed with non-FPGA modules) and you want to enable the DVI controller prior to loading the linux kernel, you can enable them with the following commands.
U-Boot > i2c mw 38 8 3F U-Boot > i2c mw 38 0x33 0x30
If you would like u-Boot to automatically enable the controller on power up, simply add them to the boot command string (separated by a semicolon).
From Linux¶
The revision C board has the I2C interface on the DVI controller chip connected directly to the OMAP-L138 (or the 1808) I2C0 controller. So all you need to do is issue the following commands:
root@mityomapl138:~# insmod fpga_ctrl.ko root@mityomapl138:~# echo 1 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOUR FPGA IS NOT ALREADY PROGRAMMED BY UBOOT, resets the FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# echo 2 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOUR FPGA IS NOT ALREADY PROGRAMMED BY UBOOT, programs the FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# cat YourFPGAImage.bin > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/image #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOU ARE PROGRAMMING THE FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# echo 3 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd # do this to probe the FPGA for the I2c controller device root@mityomapl138:~# i2cset -y 1 0x38 0x8 0x3F root@mityomapl138:~# i2cset -y 1 0x38 0x33 0x30
Step 4 - LCD Touchscreen¶
In order to get the touchscreen working, you will need to run the following commands:
root@mityomapl138:~# insmod evdev.ko root@mityomapl138:~# insmod fpga_ctrl.ko root@mityomapl138:~# insmod ads7843.ko root@mityomapl138:~# echo 1 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOUR FPGA IS NOT ALREADY PROGRAMMED BY UBOOT, resets the FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# echo 2 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOUR FPGA IS NOT ALREADY PROGRAMMED BY UBOOT, programs the FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# cat YourFPGAImage.bin > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/image #### ONLY DO THIS IF YOU ARE PROGRAMMING THE FPGA root@mityomapl138:~# echo 3 > /sys/devices/fpga_ctrl/cmd # do this to probe the FPGA for the I2c controller device
After these commands run, there should be a /dev/input directory and a /dev/input/touchscreen input below that.
Testing the Frame buffer¶
If all goes will, you will have a /dev/fb0 which is a character device with major number 29, minor number 0. This will also
show up if you cat /proc/devices.
If everything doesn't go well you may end up with your test application not working and not writing to the fb device.
1) Enter "fbset" onto your serial port and verify that settings are returned (mode "640x480-60" etc.)
2) If fbset returns "fbset: can't open '/dev/fb0': No such file or directory" then perform the following on your serial port: "rm /etc/dev/tar"
3) Reboot
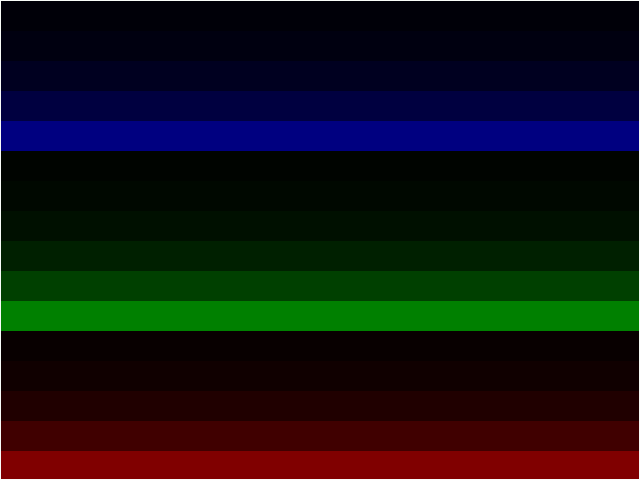
At the end of this wiki page is a simple C program source file to generate color bars on the display to help test. It divides the
screen vertically into 16 bars. Each bar represents 1 bit in a 16 bit color.
A one pixel wide white box is drawn around the display area.
Note that the 3-27-2015 version of this application allows for the use of arguments in case a different screen resolution is needed.
fbfill -w 480 -h 272
Go to top

