Qt Starter Guide 2020¶
- Table of contents
- Qt Starter Guide 2020
This guide will step you through setting up and running a simple Qt Gui Application on your MitySOM-335x system.
Prerequisites¶
- Make sure you have a VM installed.
- We currently recommend Desktop Ubuntu lts 18.04 64bit, as it has most of the requisite programs.
- August 20 2020 MDK .sh file in your hostsystem
Setup MDK¶
- Copy the MDK .sh file into the VM
- Inside the VM, open a terminal and make the file executable
chmod +x mitysom-335x-devkit-MDK-2020-08-20.sh
- Install the MDK into the VM
./mitysom-335x-devkit-MDK-2020-08-20.sh
Setup QtCreator¶
- Install QtCreator
sudo apt install qtcreator
- Install the necessary libraries and compilers
sudo apt install build-essential
- Finally, install Qt5
sudo apt install qt5-default
Once this is done, QtCreator can be started through the Ubuntu UI.
Setup CMake¶
- Install CMake
sudo apt-get install cmake
Setting Up the Kit¶
- Open Qt Creator, Note that this guide was written using Qt Creator version 4.5.2 as installed by
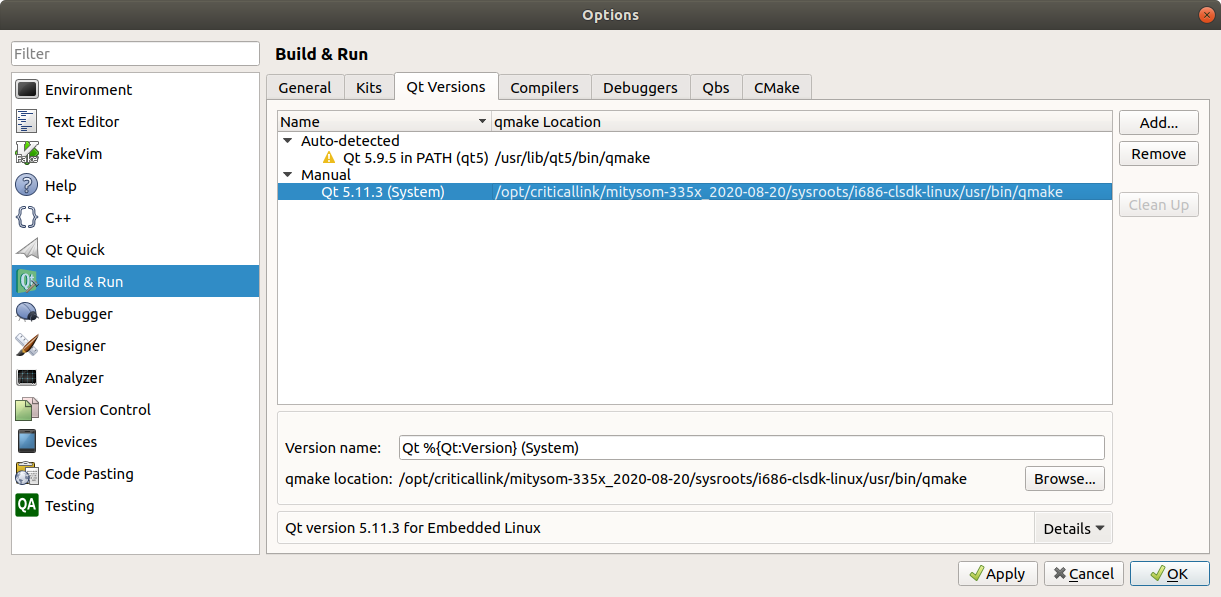
aptfrom the default Ubuntu repositories. If you are using a different version of Qt Creator, some of the settings or configurations screens may be different. Please contact Critical Link if you have difficulties applying these instructions to your version of Qt Creator. - Go to the Tools -> Options... menu and select "Build and Run" from the left options and then select the "Qt Versions" tab that is shown.
- Click the "Add..." button. Navigate to <MDK path>/sysroots/i686-clsdk-linux/usr/bin/ and click on qmake
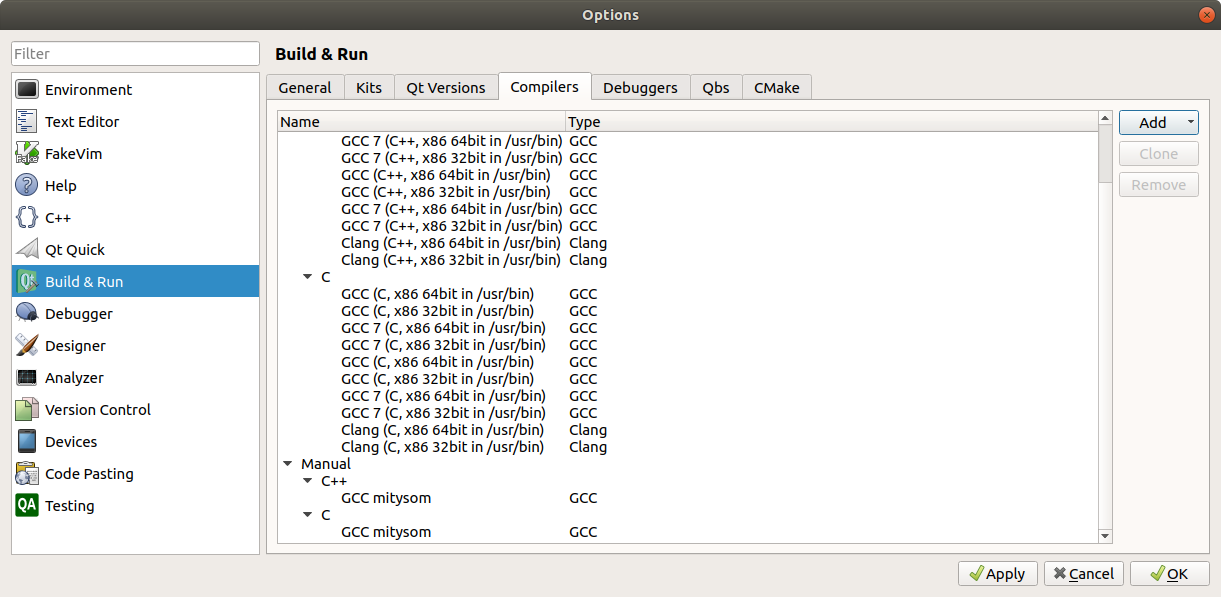
- Select the Compilers tab. Click on Add -> GCC -> C. Navigate to <MDK path>/sysroots/i686-clsdk-linux/usr/bin/arm-criticallink-linux-gnueabi/ and select arm-criticallink-linux-gnueabi-gcc. Give it an easily recognizable name, as we will need it later.
- Click Add again, but this time select GCC -> C++. Navigate to <MDK path>/sysroots/i686-clsdk-linux/usr/bin/arm-criticallink-linux-gnueabi/ and select arm-criticallink-linux-gnueabi-g++. Give this one a recognizable name as well.
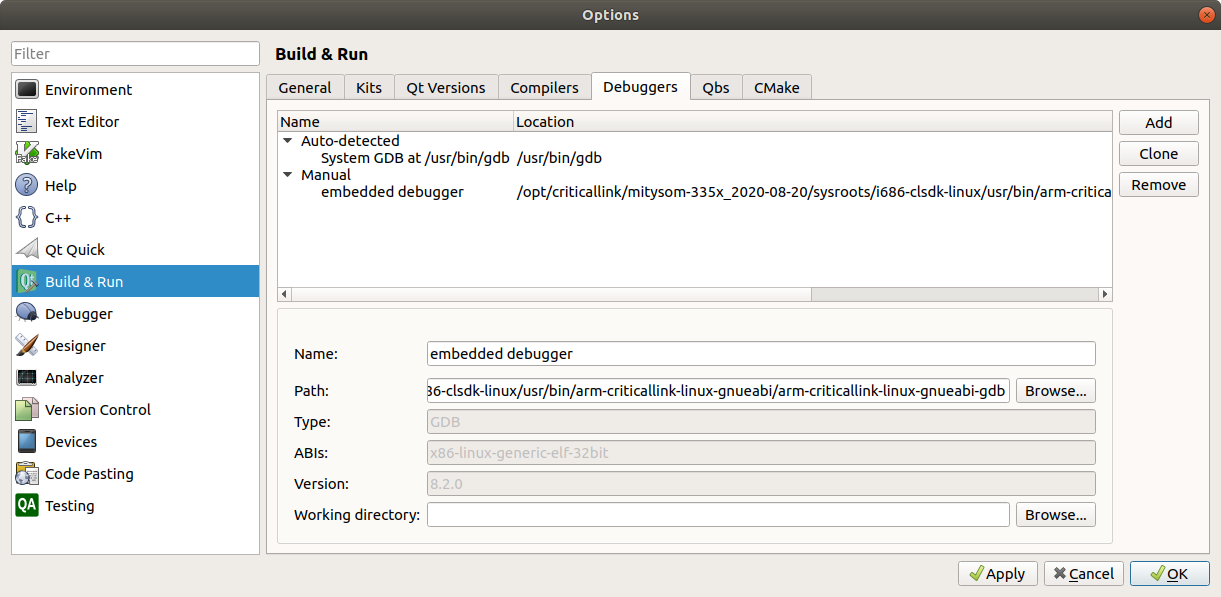
- Select the Debuggers tab. Click on Add and give the new debugger an easily recognizable name. Click on browse next to path and navigate to <MDK path>/sysroots/i686-clsdk-linux/usr/bin/arm-criticallink-linux-gnueabi/ and select arm-criticallink-linux-gnueabi-gdb
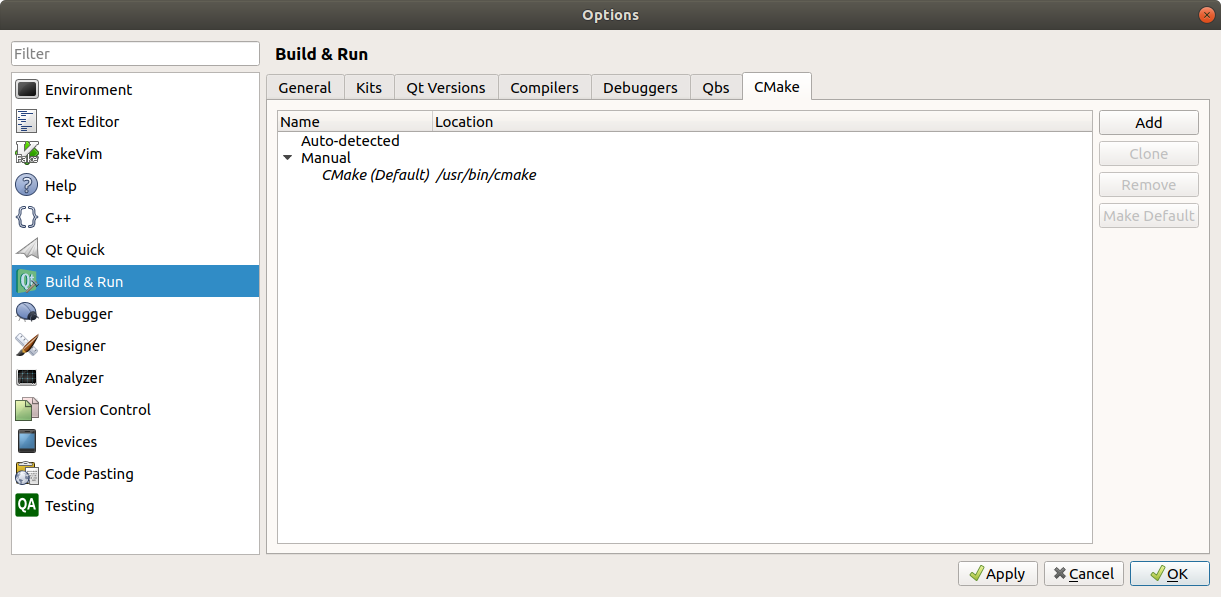
- Select the Compilers tab. Confirm that CMake is under Auto-detected. If it is not, click Add and then click newly-created NewCMake under Manual. Change the name to CMake and the path to /usr/bin/cmake.
- Select Devices from the left options. Under the Devices tab, click on Add... and select Generic Linux Device. Choose a name, and enter the IP address of the devkit and root as the username, leaving password blank. If the test fails, you will not be able to deploy into the devkit from QtCreate.
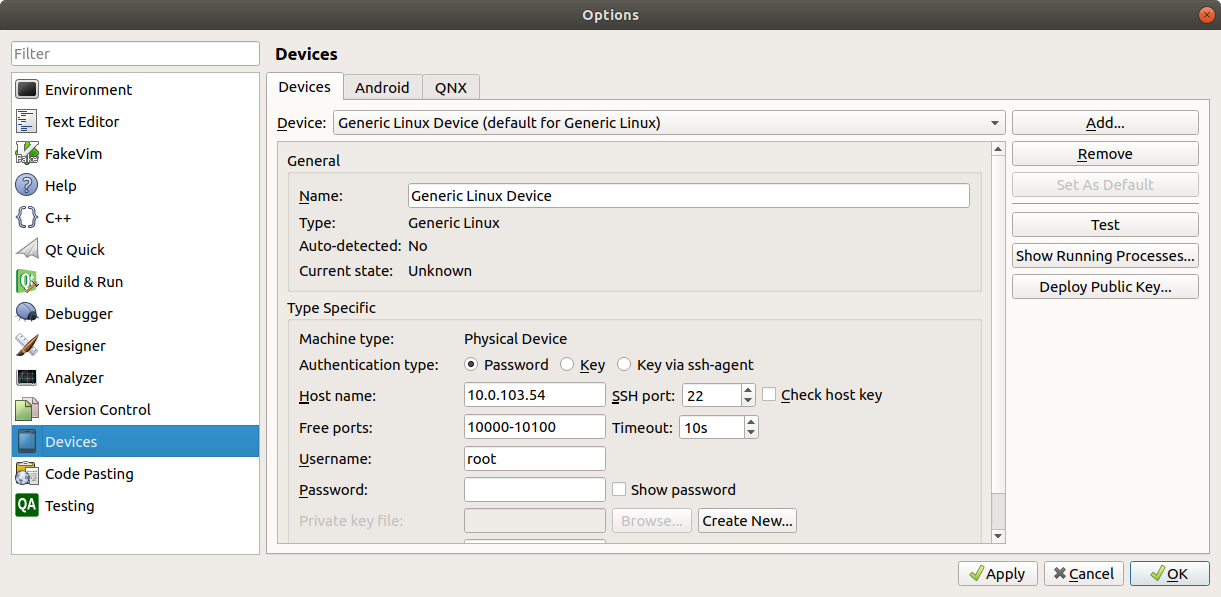
- Return to Build and Run in the left options and navigate to the Kits tab. Click on Add and fill in the options with the components from previous steps. For Sysroot, navigate to and select <MDK path>/sysroots/cortexa8t2hf-neon-criticallink-linux-gnueabi/.
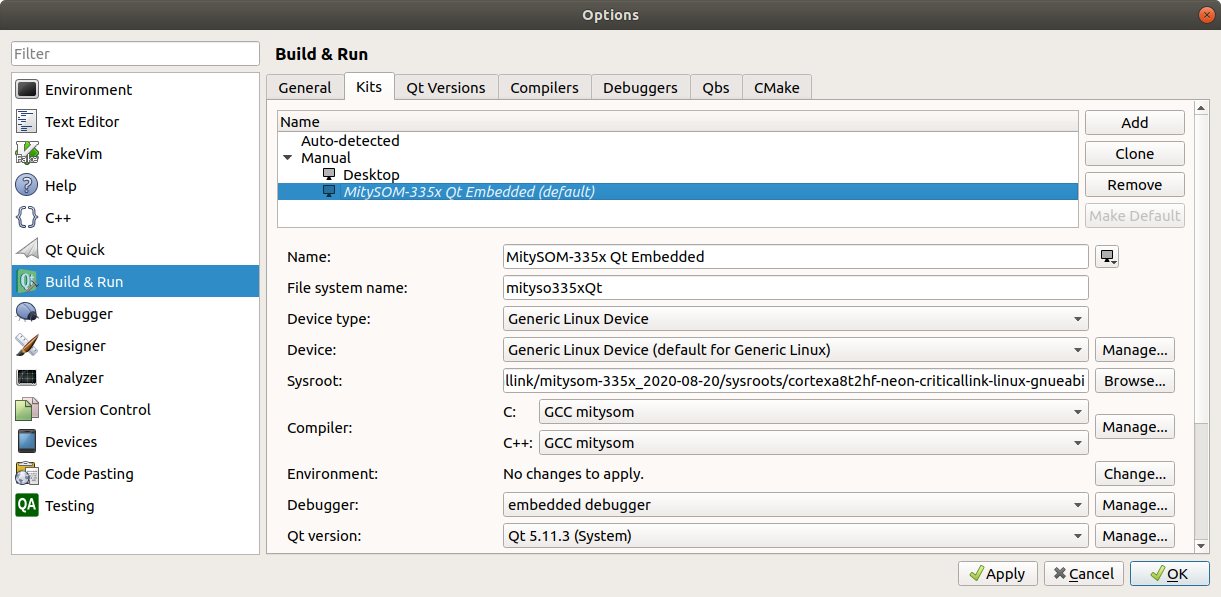
- Click OK to return to the Welcome page.
Building and Compiling the GUI¶
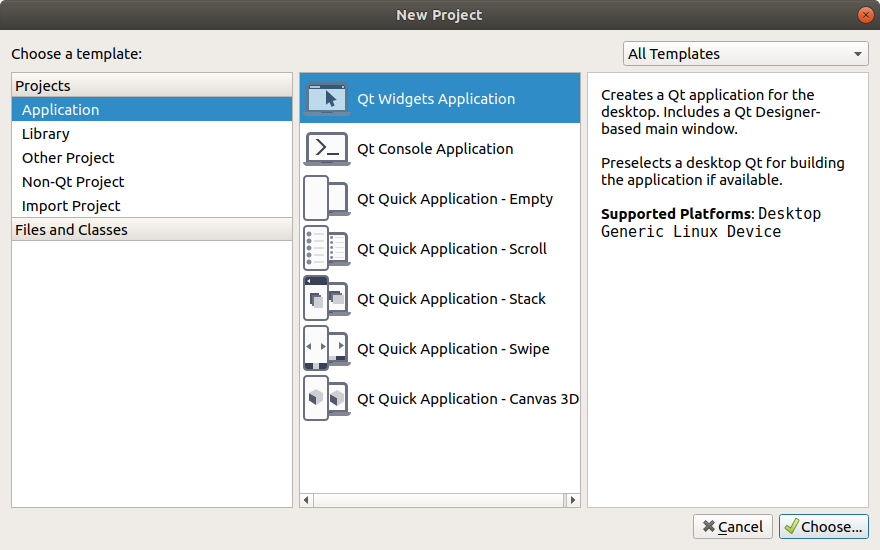
- In the Welcome page click on new project.
- Choose Qt Widgets Application and click Next
- Give the project a name "HelloWorld" and press browse next to Create in, to create a new folder "projects"
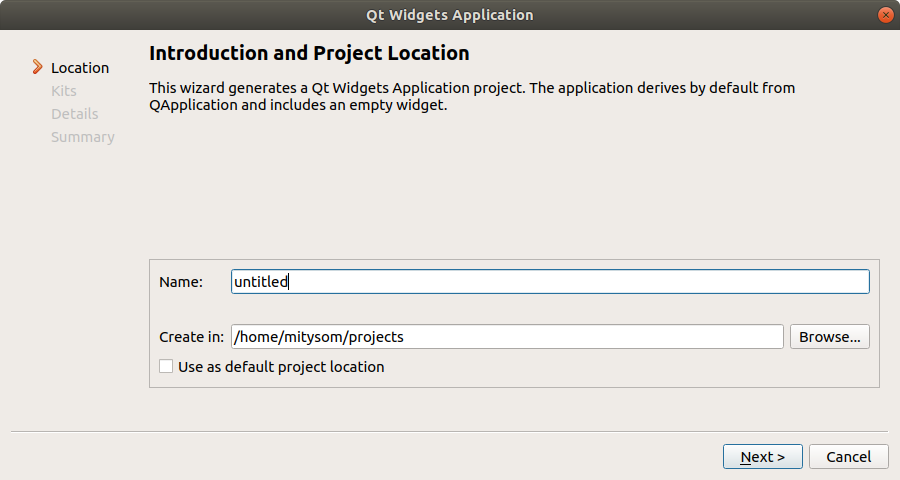
- In Kit selection, select the kit created the previous steps. Keep desktop selected so you can run and test the program in the VM.
- Continue to click next and then finish.
- Expand the project source tree and inside 'Forms' double-click on 'mainwindow.ui. This will open the Design view.
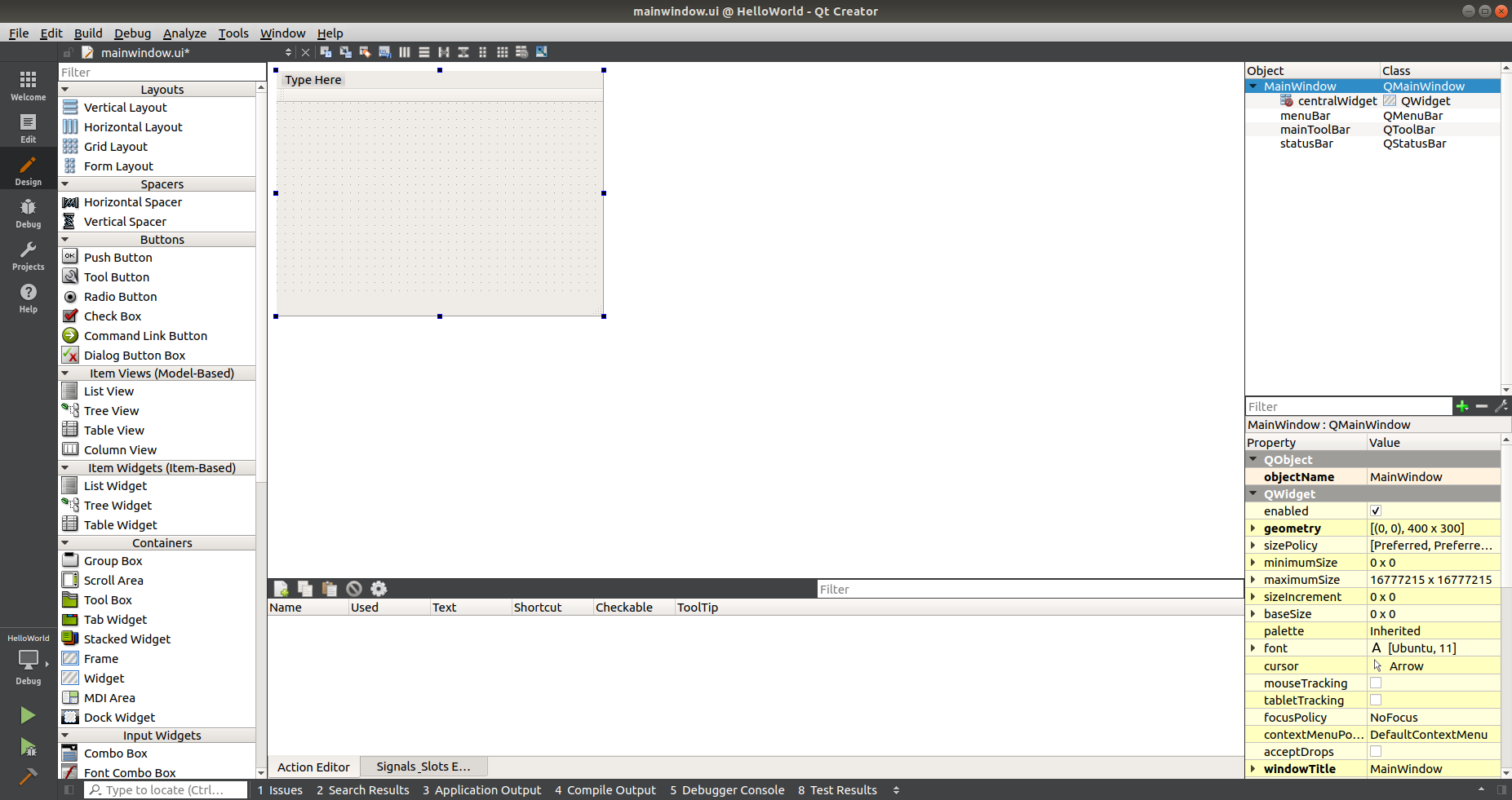
- Drag and drop a 'Line Edit' Input Widget from the left hand pane onto the central pane.
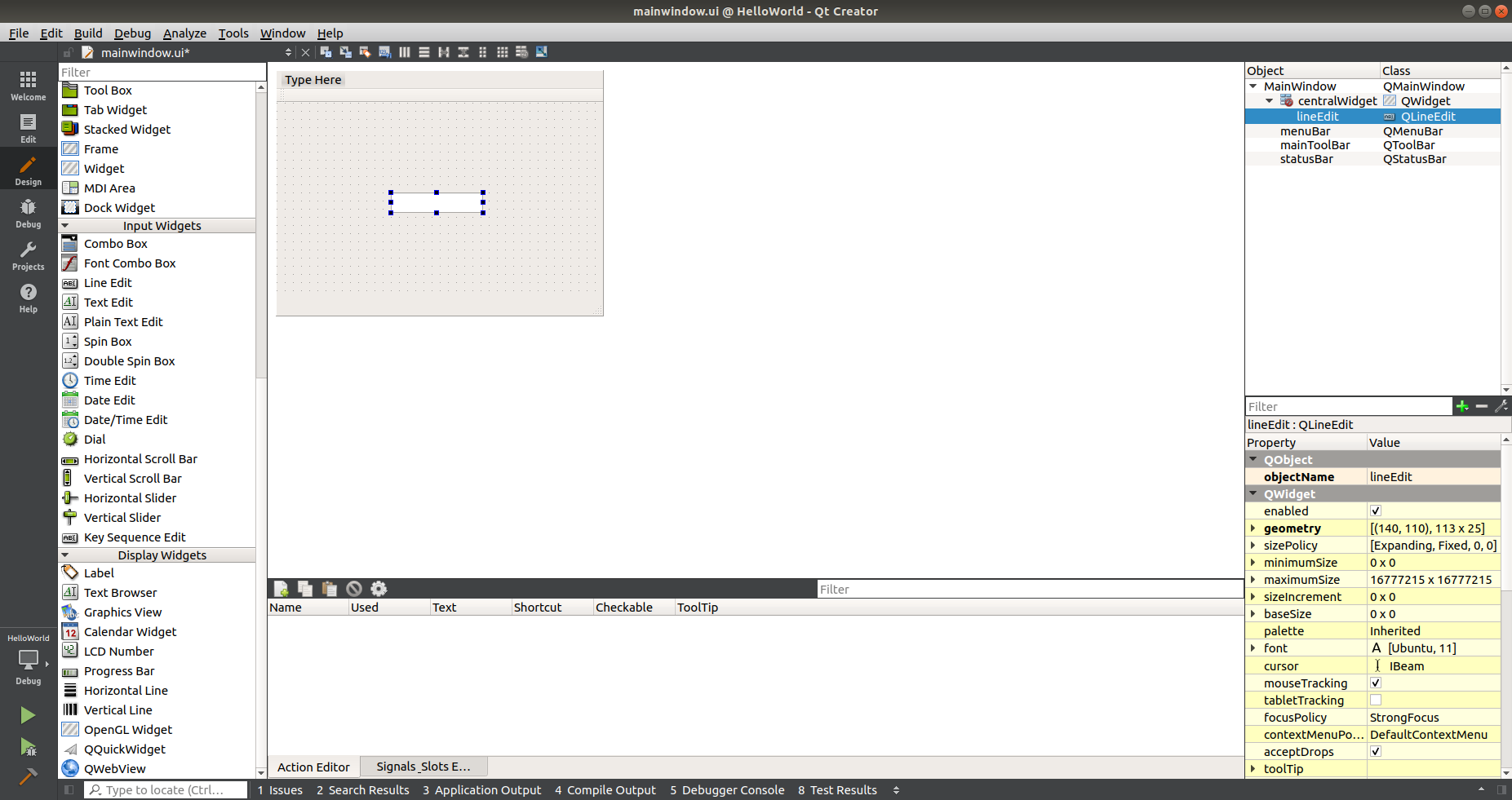
- Click on the 'Edit' in the left hand column of Qt Creator.
- In the project source tree, double-click on 'mainwindow.cpp' in the 'Sources' directory.
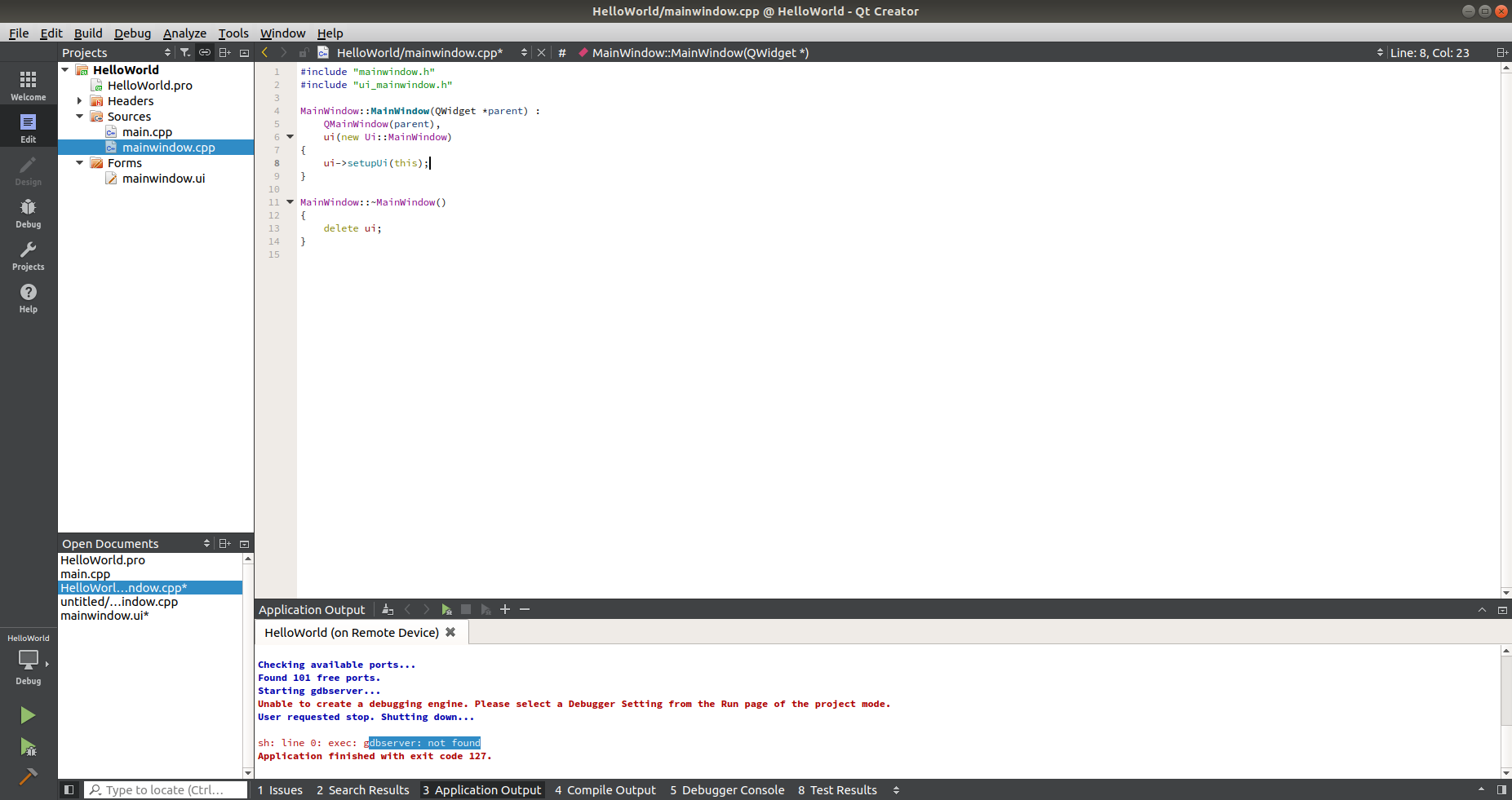
- Add 'ui->lineEdit->insert("Hello World!");' to the MainWindow class constructor.
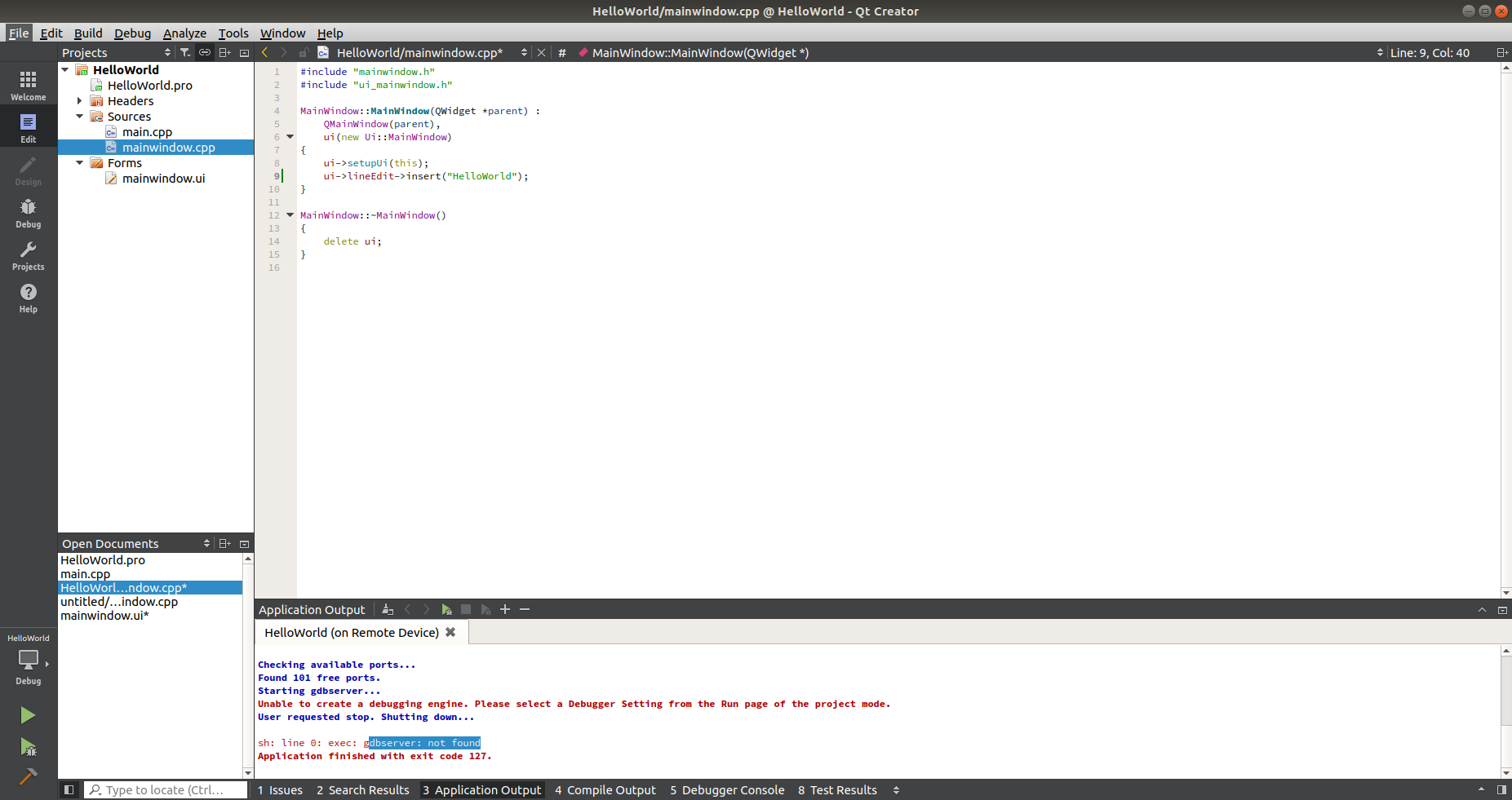
Running the GUI on the MitySOM-335x from QtCreator¶
- While on the project, click the Edit button on the left
- add the following lines to HelloWorld.pro
TARGET = Test target.files = Test target.path = /home/root INSTALLS += target
Manually Building the project for ARM¶
If Qt Creator is having issues building, you can run the steps yourself. Otherwise, the QTCreator built files are usually found in the project folder in a folder named "build-<Kit Name>-debug"
- Open a terminal
source <MDK path>/environment-setup-cortexa8hf-neon-criticallink-linux-gnueabi
- Navigate to the project directory
cd projects/HelloWorld
- Run qmake to allow Qt to generate a Makefile
qmake
- Run make to build the project
make
- The compiled file will be HelloWorld. Use the
filecommand to verify it was build for ARM> file HelloWorld HelloWorld: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), for GNU/Linux 2.6.16, not stripped
- Transfer file to the devkit. Replace <ip address> with ip of device. This will place the file in the home directory: /home/root/
scp HelloWorld root@<ip address>:
Running the GUI on the MitySOM-335x¶
- Run the application from the devkit
root@mityarm-335x ~ $ ./HelloWorld -platform linuxfb
QT Tips¶
Easier cross platform builds¶
Placing the following in your projects .pro file allows for easier development of your application for running on both your PC and 335x.
contains(QT_ARCH,arm) {
DEFINES += HOST_ARM
CONFIG += arm # Add arm so we can use arm {}
}
It allows you to use #ifdef HOST_ARM in your code around sections that can't run on your PC. For example code that touches the gpio.
The "CONFIG += arm" line allows you to easily specify configurations in your .pro file that only apply when cross compiling. Example:
arm {
SOURCES += arm_only_code.cpp
}
Have application show up full screen on 335x¶
- Add the following to the main window constructor. Assumes you've included the above tip.
#ifdef HOST_ARM this->showFullScreen(); #else this->setFixedSize(800,480); // Set this to expected screen resolution #endif
Go to top

